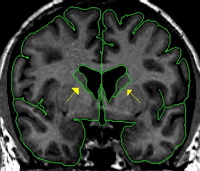
The caudate is a C-shaped structure with an enlarged head deep in the frontal lobe and an increasingly attenuated body and tail which follow the lateral ventricle around into the temporal lobe. We do not consider the tail of the caudate in the CMA method. In the coronal view the caudate appears lateral to the lateral ventricles in each hemisphere. The caudate begins very small and reaches its largest extent in the early to mid region and grows smaller as you travel more posterior until it finally disappears. The caudate is bordered inferiorly by white matter, the thalamus (when present), or the nucleus accumbens (when present). The caudate is bordered superiorly by the transverse fibers, or white matter. Laterally, the caudate is bordered by white matter. The medial border is the lateral ventricle.
Procedure
Segmentation
The histogram method is used for creating the caudate outline.
Part I - Anterior portion of the caudate
The histogram box should extend from the gray matter at the center most point of the caudate into the surrounding white matter. Approximately equal amounts of both gray matter and white matter should be included in the box. It is important not to include the transverse fibers that run along the superior edge of the caudate. These fibers should be excluded from both caudate and lateral ventricle. We also do not extract the vertical portion or the tail of the caudate.
Anteriorly, there is some partial voluming, so care should be taken not to overestimate the caudate. Projection lines should be used to determine the true extent of the caudate
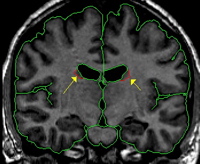
Posteriorly, it is often difficult to get a useful histogram, so intensity contour can be employed.