
Part IA – Vermal Lobules l-V
General Description
The cerebellum is located anterior to the brainstem and inferior to the cerebrum.
The cerebellum can be sectioned into the vermis and the right and left hemispheres.
Between the cerebellum and the brainstem, and between the left and right
hemispheres of the cerebellum is the 4th ventricle. Although the cerebellum
is anterior to the brainstem, the brainstem and cerebellum often show up
on the same coronal slices due to the fact that the cerebellum curves around
the brainstem. The cerebellum is surrounded by external dura, the transverse
sinus, and other non-brain tissue. Because of its location close to the brainstem
and the base of the brain, there are many nerves and blood vessels.
Segmentation Procedure
The cerebellum is extracted by using the intensity contour function. The correct
contour for the outline is usually the same as the outline for the cerebral
exterior. In order to see the full extent of the cerebellum it is helpful
to increase the brightness of the screen similar to the brightness used for
the cerebral exteriors. Sulci lines are in the sagittal view to determine
the vermal lobules. The cerebellum is segmented into three vermal lobules
(l-V, Vl-Vll and Vlll-X) as well as the right and left hemispheres.
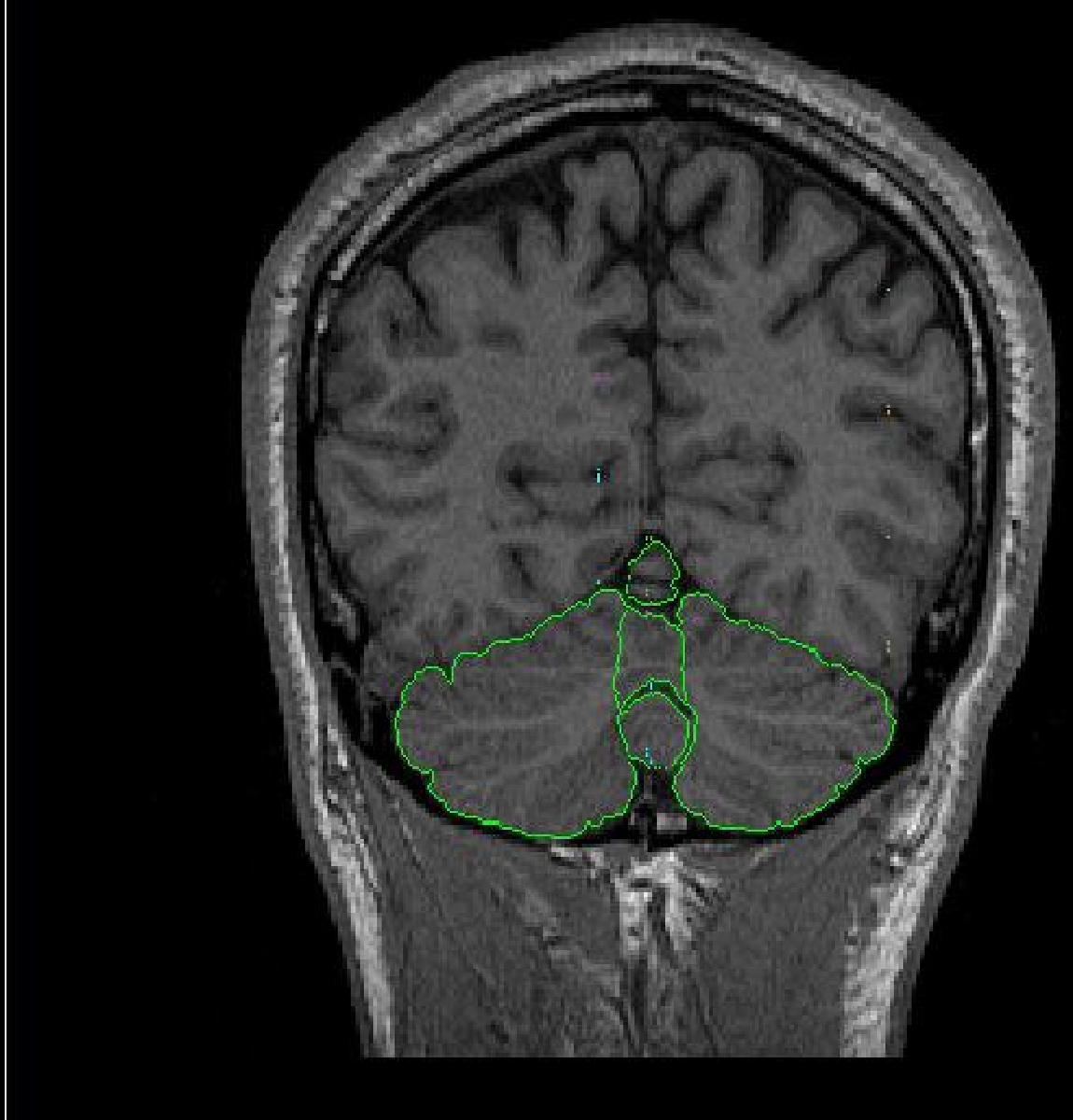
The vermal lobules are segmented into 3 sections including lobules l-V, Vl-Vll and Vlll-X. Sulci lines will be drawn in the sagittal view to determine the borders for the vermal lobules. Lobule l-V is determined by finding the sagittal view containing three distinct sections of the cerebellum. The top most anterior section includes lobules l-V. Lobules l-V are determined by all structures lateral to the primary fissure.
Part IB- Vermal Lobules Vl-Vll

The vermal lobules Vl-Vll are determined by drawing sulci lines in the sagittal
view from the medial aspect of the primary fissure to the lateral aspect of
the prepyramidal fissure.

Part lC – Vermal Lobules Vlll-X
The vermal lobules Vlll-X are determined by drawing sulci lines in the sagittal
view from the lateral aspect of the prepyramidal fissure to the precentral
fissure.

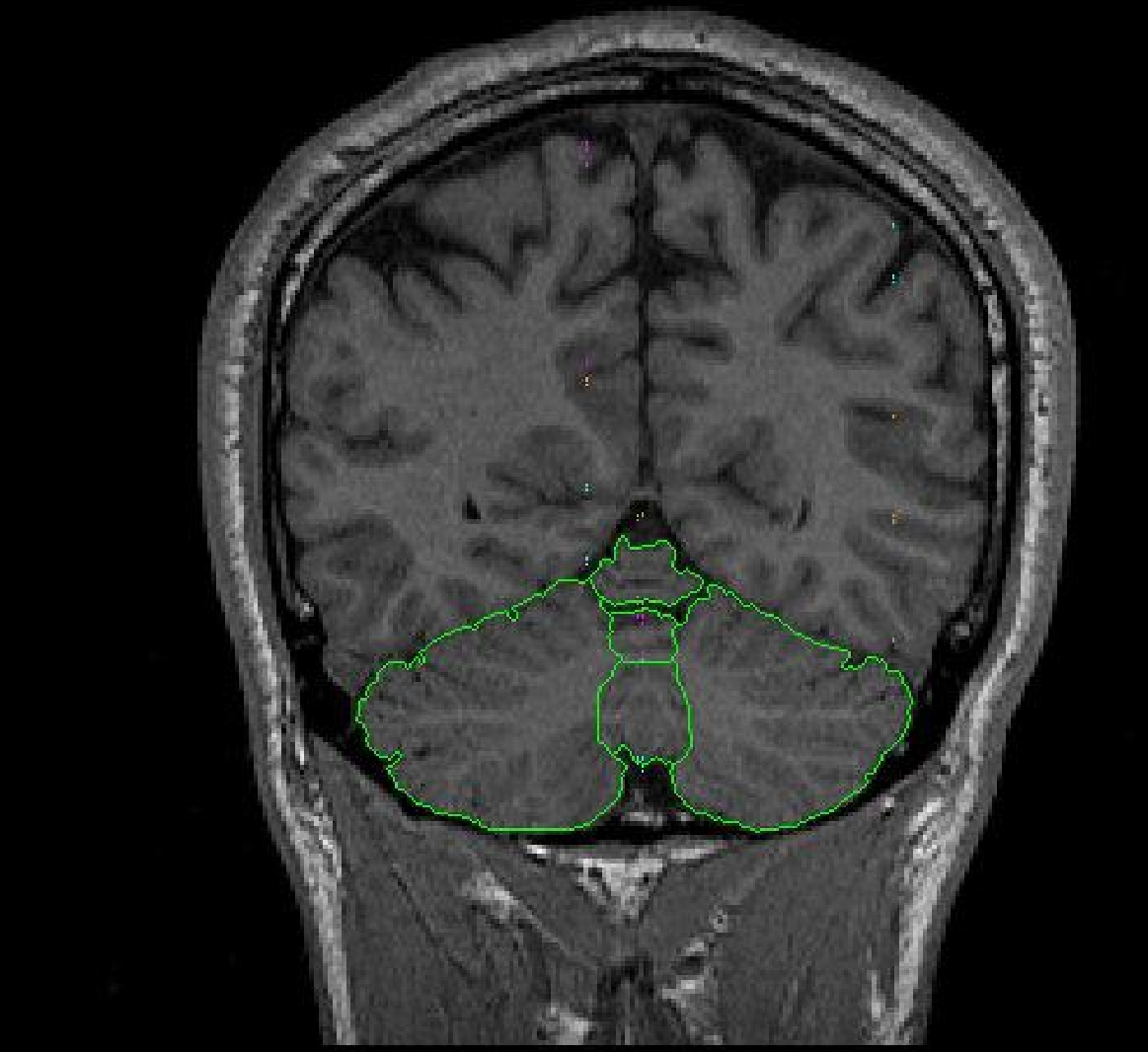
Part llA. – Cerebellar Hemispheres
The cerebellar hemispheres are defined as the areas not included in the vermal
sulci lines.
 Part IIb - Cerebellum hemispheres
Part IIb - Cerebellum hemispheres
Use the contour function to define the exterior of the cerebellum. Use the draw function to exclude any non-brain tissue, as well as to draw in the midline. Extract the right cerebellum hemisphere exterior and left cerebellum hemisphere exterior separately.
Using the projection lines and alternate views is important to determining
the cerebellar borders. One difficult area is the
 posterior
extreme of the cerebellum, as well as the sinuses that run along the tips
of the lateral cerebellum wings in the cerebellar contour. These sinuses
will be superior to the cerebellum and may be mistaken for cerebellum.
posterior
extreme of the cerebellum, as well as the sinuses that run along the tips
of the lateral cerebellum wings in the cerebellar contour. These sinuses
will be superior to the cerebellum and may be mistaken for cerebellum.
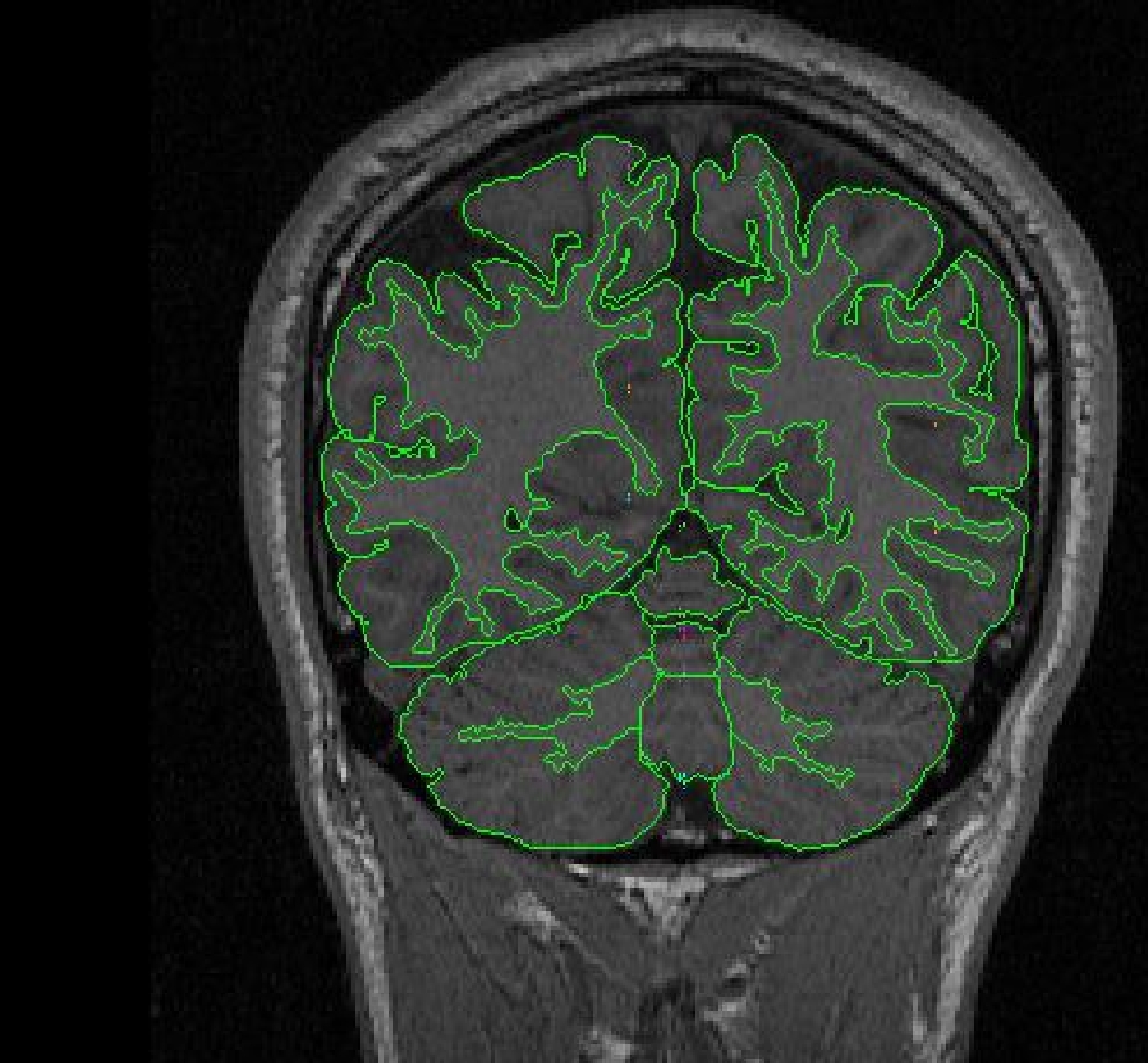
Labeling
The vermal lobules are labeled as l-V, Vl-Vll and Vlll-X. The cerebellar hemispheres
are labeled as right and left cerebellar hemispheres and the white matter is
labeled cerebellar white matter.
© 2005 Neuromorphometrics, Inc. All rights reserved.