General Description
The pallidum is the another subdivision of the lenticular nucleus (the other is the putamen). As seen from the axial view the lenticular nucleus resembles a rounded triangle. The pallidum makes up the smaller medial part of this triangle.
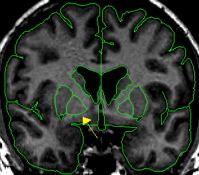
In the coronal view the pallidum resembles a rounded triangle that continues off the putamen. The pallidum starts anteriorly as a small triangle and reaches its largest extent in its most medial slices and then dwindles to a small triangle again in the most posterior slices.
The pallidum is essentially surrounded by white matter except for the lateral border which is the putamen. The putamen and pallidum are separated at this border by a thin strip of white matter called the lateral medullary lamina. Medially, pallidum is difficult to discern from the surrounding white matter because although it is gray, in terms of its intensity, its darkness is frequently fainter than putamen.
Procedure
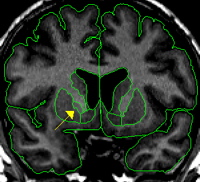
Segmentation
The pallidum should be extracted using the intensity contour function.
Part I - Putamen and pallidum
It is helpful to extract the putamen first, in one hemisphere, then only slightly adjusting the same contour line, and extract pallidum in the same hemisphere. Since the pallidum and putamen share a border, it is helpful to use the axial view to accurately discern between the two structures. The thin strip of white matter (the lateral medullary lamina) that separates these structures should be extracted as part of pallidum.